Glyphosate
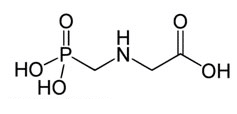
The chemical formula of glyphosate
Since glyphosate is a systemic agent that works throughout the entire plant, it is not surprising that the substance also remains in the plant. Degradation in plants is small, which is why the maximum amount of glyphosate allowed in our food has been increased by the government to 1000 times in recent years. Remarkably high amounts of glyphosate have been permitted since 1994 in various grains (up to 20 mg/kg) and beef and sheep kidneys (2 mg/kg). It has been shown to be present in the entire body of humans and animals, therefore in the urine, organs and even in the bone marrow. In animals it is slowly but surely becoming clear that it has a major impact on health and reproduction:
Neutralizing effect of humic acid
Humic acids have a neutralizing effect on toxins produced by bacteria (82%). They also absorb heavy metals, nitrates, fluorides, organic phosphates (parathion methyl, glyphosate, organic chlorine insecticides, carbarl and warfarin). The University of Leipzig has tested the neutralizing effect of humic acids at various concentrations of glyphosate. These tests show that several humic acids are able to neutralize glyphosate (however, not all of them can). This effect has also been investigated in dairy cattle, where humic acid was shown to be able to neutralize glyphosate as well. The effect of glyphosate on the bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract was neutralized. Our product PrimeHumic has been tested by the University of Leipzig and turned out to be very capable of neutralizing the negative effects of glyphosate on intestinal health.

Humus


